
Unlock the possibilities of your medical education at mdcat1.com! Examine a large collection of 1ST YEAR KMC PHYSIOLOGY OSPE 2.
KMC PHYSIOLOGY OSPE 2
Station no: 1
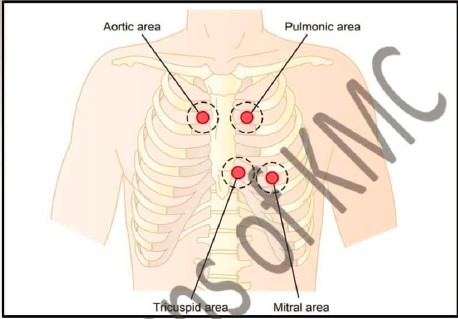
| 1. Name the condition in which first heart sound become loud |
| 2. Why fourth heart sound is recorded |
| 3. What is difference in 1st and 2nd heart sound |
| 4. At which area we can auscultate fourth heart sound |
Station no: 2
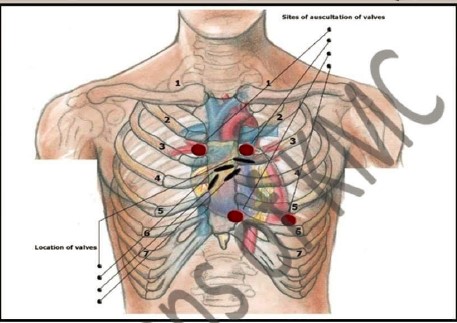
| 1. Give the names of valves shown by arrows in this picture |
| 2. How second heart sound produced |
| 3. In which area Mitral valve situated |
| 4. Which six points are noted when we auscultate the heart sound |
Station no: 3
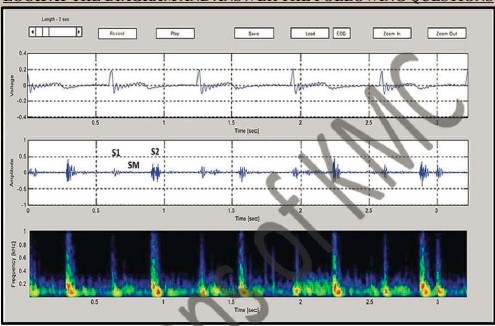
| 1. What is the name of this machine |
| 2. In which process this machine is used |
| 3. How many types of heart sound |
| 4. Give the names of added heart sounds |
Station no: 4
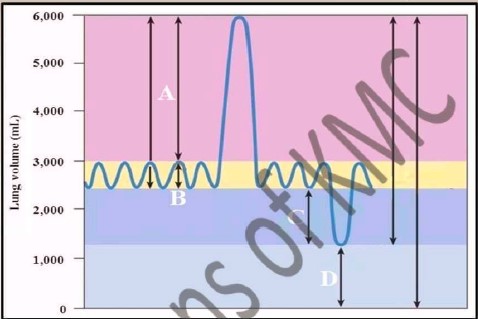
| 1. What does A, B, C and D shows in the diagram |
| 2. What is spirogram |
| 3. What is pulmonary volume and pulmonary capacity |
| 4. What is functional residual capacity and which volume is included |
Station no: 5
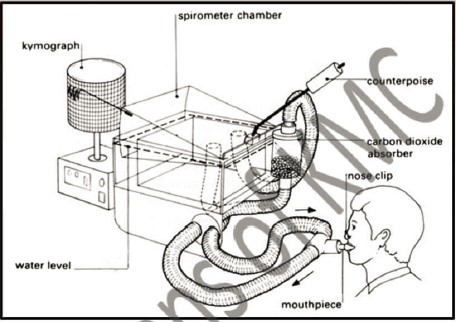
| 1. What is spirometry |
| 2. Define vital capacity. What is its normal value |
| 3. In which condition vital capacity is descreased |
| 4. Define residual volume and what is its normal value |
PHYSIOLOGY OSPE Station no: 6
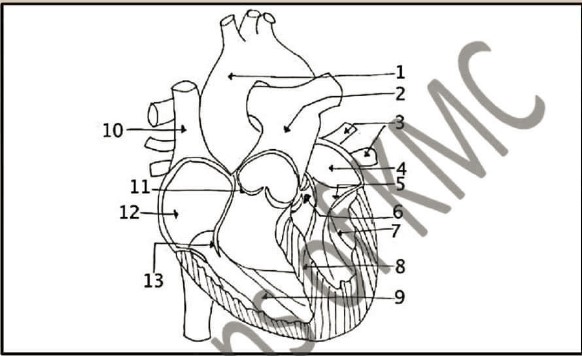
| 1. Label the above diagram of the heart. How many action of the heart |
| 2. How many stages of cardiac cycle |
| 3. What is normal heart rate and how much blood pumped by the heart per ventricle per minute |
| 4. Define refractory period and its types |
Station no: 7

| 1. Label the above diagram and what is the time duration between each wave of ECG |
| 2. Define ECG and ECG leads |
| 3. What are the uses of ECG |
| 4. What are the causes to produce each wave of ECG |
Station no: 8
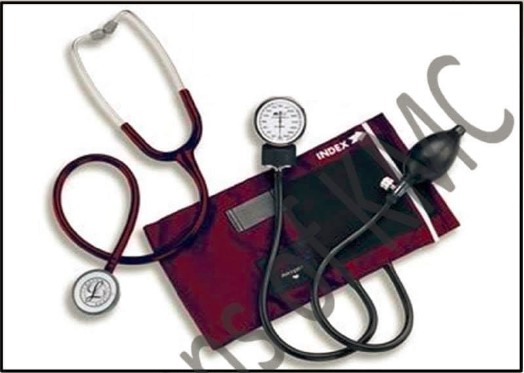
| 1. Label the above diagram and define pulse pressure and mean blood pressure |
| 2. Define total peripheral resistance and how it is controlled |
| 3. How the blood pressure is regulated |
| 4. How many phases (sounds) when we monitor the blood pressure |
Station no: 9
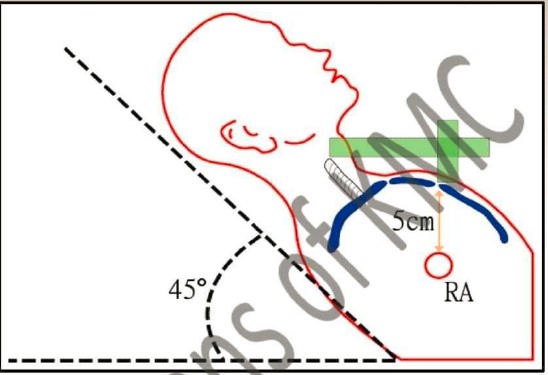
| 1. Which vein is selected for JVP measurement |
| 2. Define JVP and what is normal value for JVP |
| 3. Define the x and y wave in JVP |
| 4. Give any 2 causes for raised JVP |
Station no: 10
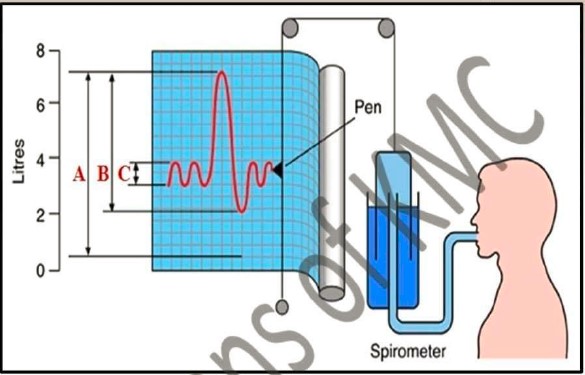
| 1. What does A, B, C and D shows in the diagram |
| 2. What is Tidal volume |
| 3. What is vital capacity |
| 4. Which method is used for the measuring functional residual capacity |
Station no: 11
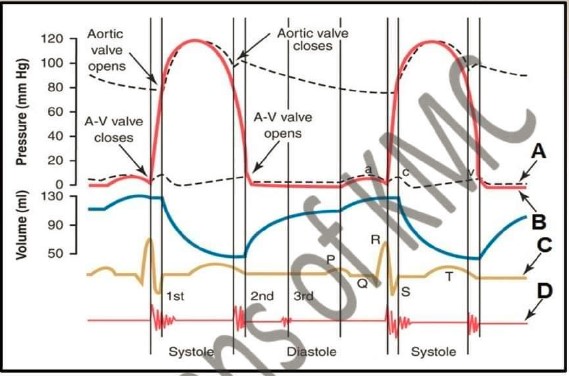
| 1. What does A, B, C and D shows in the diagram |
| 2. What is cardiac cycle |
| 3. Define isovolumic ventricular relaxation period |
| 4. Define systole and Diastole |